The Atlantic Croaker, renowned for its distinctive vocalizations, is often a topic of discussion among fishing enthusiasts and marine biologists alike. As a species predominantly found in coastal waters extending from Massachusetts to Mexico, it raises the question of whether the Croaker is inherently a saltwater fish.
While its presence in such environments might suggest this conclusion, does its classification as a saltwater species tell the full story of its lifestyle, dietary habits, and overall significance in the ecosystem? The answer may be more complex than expected, inviting further exploration into the fascinating world of the Croaker.
Key Takeaways
- Yes, Croaker is a saltwater fish, primarily inhabiting the Chesapeake Bay region and the Atlantic coast.
- They thrive in estuaries and coastal waters with sandy or muddy bottoms, forming large schools.
- Croaker fish are known for their distinctive croaking noise and are part of the drum family under the Perciformes order.
- Being abundant in the ecosystem, their presence indicates health of the coastal and estuarine environments.
Understanding the Croaker Fish
What exactly is the Croaker fish, a popular saltwater species known for its unique croaking noise when out of water, predominantly found in the Chesapeake Bay region? The Croaker, also referred to as hardhead, is a sought-after quarry for fishermen in the Chesapeake Bay watershed, a rich and diverse ecological area. It's renowned for its distinctive auditory display, a croaking noise that it produces when out of water, a characteristic that lends itself to the fish's common name.
This saltwater species is seasonally distributed from the Atlantic coast to the upper bay and tidal rivers, thereby creating a sense of regional belonging and unity among the local angler community. The fish's migratory patterns and habitats are intrinsically tied to the health and biodiversity of the Chesapeake Bay, making it a vital component of this complex ecosystem.
Anglers usually catch Croaker along shorelines, fishing piers, and deep channels in specific locations within the bay and tidal rivers. This emphasizes the Croaker's importance not only as a species in the marine ecosystem but also as a social and economic asset for the local communities. Understanding the Croaker fish is thus crucial to preserving the environmental and socio-economic health of the Chesapeake Bay region.
Croaker's Scientific Classification
The Croaker is a member of the Sciaenidae family, under the Perciformes order.
The genus designation 'Micropogonias' stems from the presence of minuscule beard-like appendages on the fish's chin.
The species name 'undulatus' is indicative of the wavy bars observable on the upper sides of these marine organisms.
Croaker's Species Classification
Have you ever pondered the scientific classification of the Atlantic Croaker, a member of the Sciaenidae family which encompasses both drum and croaker species?
The Atlantic Croaker, scientifically known as Micropogonias undulatus, belongs to the genus Micropogonias, a cluster of croaker species indigenous to the western Atlantic Ocean. The nomenclature 'Micropogonias' translates to 'small beard', while 'undulatus' reflects the species' wavy physical appearance.
Known for their distinctive croaking noise, Atlantic Croakers form an integral part of the drum family. Understanding the scientific classification of these croaker species is pivotal for a detailed study of their biology, behavior, and the ecological role they play in marine ecosystems. This analytical approach fosters a sense of belonging for those passionate about marine life.
Croaker's Habitat Analysis
Dwelling primarily in estuaries and coastal waters with sandy or muddy bottoms, the Atlantic Croaker, Micropogonias undulatus, is a saltwater fish that plays a vital role in the marine ecosystem as both a bottom feeder and a prey for larger predators. Its habitat, characterized by saline waters and sediment-rich substrates, offers ideal conditions for this species' survival and proliferation.
Named for their distinctive croaking noise, an auditory display that signals their presence and dominance, these fish are integral components of their ecosystems' food chains. Understanding the Atlantic Croaker's habitat is crucial for population management strategies, as changes in environmental conditions can significantly affect their distribution and, consequently, the balance of the marine ecosystem. This analysis illustrates the interconnectedness of species and habitats in maintaining biodiversity.
Identifying Features of Croaker
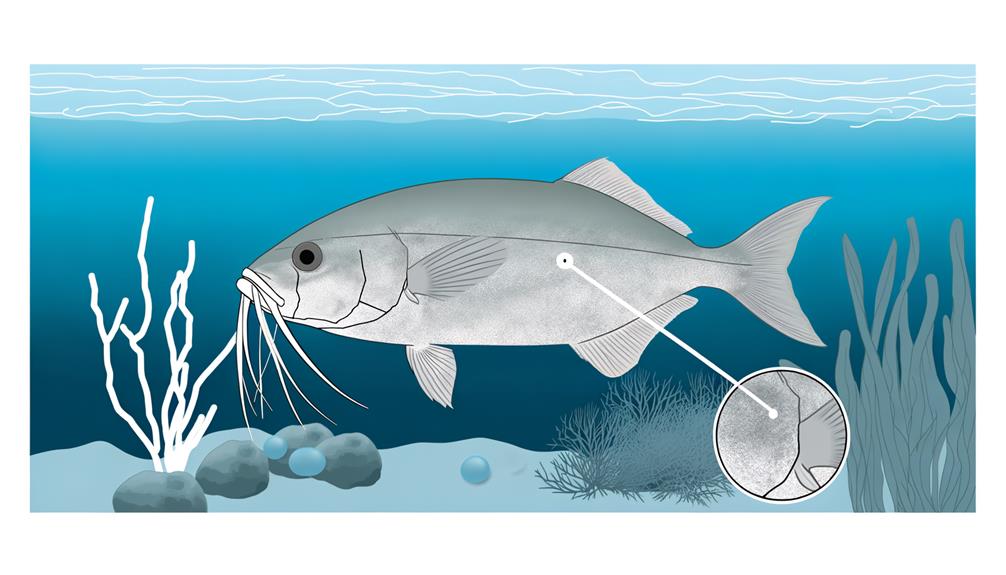
Recognizing the distinct features of the Croaker, a saltwater fish famed for its unique croaking noise, requires careful attention to its physical characteristics ranging from its prominent lateral line to the distinctive barbels on its chin. The croaking noise they make is a significant feature that sets them apart from other marine species. This auditory characteristic, however, is only an aspect of the Croaker's complex physical identity.
Adult Croakers exhibit a color gradient that transitions from a pinkish to coppery back, fading to a silver/white on their sides. These color transitions are punctuated by dark vertical bars along their upper sides. On the other hand, juvenile Croakers possess an iridescent hue and have serrated gill plates, a feature that gradually disappears as they mature.
Another notable feature is their downturned mouth, indicative of their bottom-dwelling lifestyle in estuarine and coastal waters. The Croaker's three to five chin barbels, often compared to whiskers, play an essential role in detecting prey in their sedimentary environments.
Comprehensively, these features coalesce to form the unique identity of the Croaker, a fascinating specimen in the realm of saltwater fish. Understanding these features enables a deeper appreciation of the Croaker's place in the aquatic world.
Croaker's Natural Habitat
In addition to their unique physical characteristics, understanding the Croaker's natural habitat—namely the coastal waters of the western Atlantic Ocean—offers further insight into this intriguing saltwater species. This fish is commonly found in bays and estuaries, preferring areas with sandy or muddy bottoms. The habitat selection is not arbitrary; it is driven by the availability of their primary food sources, which include polychaete worms, crustaceans, and small fish.
From a broader geographical perspective, the distribution range of Croaker spans from Massachusetts to Mexico along the Atlantic coast, illustrating the species' adaptability to different marine environments. Seasonal changes also affect their habitat choice. For instance, they visit the Chesapeake Bay from March to October, moving in and out with the changing seasons.
This understanding of the Croaker's natural habitat not only enhances our appreciation of this saltwater species but also underscores the importance of preserving these coastal areas. By protecting these habitats, we ensure the continued existence of the Croaker and countless other marine species that share these waters.
Behavior and Lifestyle of Croaker

Croaker exhibit a characteristic vocalization, often described as a drumming or croaking sound, that is distinct among marine species.
Their daily activity revolves around bottom feeding, primarily comprised of shrimp, crabs, and detritus, contributing to their ecological role in coastal waters.
Furthermore, the migration patterns of croaker, which involve spawning in large offshore gatherings during fall, underscore the species' complex behavior and lifestyle.
Croaker's Unique Vocalization
One of the most distinctive features of the croaker, setting it apart from other saltwater fish species, is its unique ability to produce croaking noises, particularly when it is out of water. This phenomenon, known as the croaker's unique vocalization, is produced by the action of specialized muscles vibrating against the swim bladder.
This mechanism allows the croaker to produce its distinctive croaking sound that is unmatched in the aquatic world. Among the drum family, croakers are recognized as the loudest, a fact that brings a sense of pride to anglers who catch them. This salient characteristic not only differentiates croaker from other species but also serves as a fascinating aspect of their behavior and lifestyle.
In essence, the croaker's vocalization is an integral part of their identity, reinforcing our sense of connection with the natural world.
Daily Activity Patterns
Exhibiting a fascinating pattern of daily activities, croaker fish are known to migrate inshore and offshore during different seasons, a behavior that significantly contributes to their survival in saltwater habitats. These movements are intricately timed with the diurnal and nocturnal cycles, demonstrating an adaptive response to environmental cues.
Predominantly bottom feeders, croakers search for food such as shrimp and crabs in coastal waters. Their social behavior is also noteworthy; they form large schools, particularly during the spawning season, enhancing their chances of survival and reproduction.
Unique among fish, croakers produce a drumming or croaking sound, a distinctive characteristic of their daily activities. This complex interplay of behavior and environmental factors underscores their adaptability to marine ecosystems.
Habitat and Migration Patterns
As we move our focus from their daily activities, it becomes equally important to explore the habitat and migration patterns of the croaker, as these aspects significantly influence their behavioral and lifestyle characteristics. The defining habitats of croaker are coastal estuaries and bays, specifically in regions like North Carolina.
- Seasonal Migration: Croaker move offshore during winter and return to estuaries and bays throughout the rest of the year.
- Habitat Preference: Adults favor mud, sand, and shell bottoms, while juveniles inhabit estuarine and coastal waters.
- Feeding Habits: They are bottom feeders, consuming polychaete worms, mollusks, small crustaceans, and occasionally small fishes.
Understanding these patterns and preferences provides crucial insights for their conservation and sustainable management.
Croaker's Role in the Ecosystem

In the complex web of the saltwater ecosystem, croakers, particularly the Atlantic croaker, play a pivotal role, serving as a crucial link in the food chain by providing nourishment for larger predators. Their existence assists in maintaining the equilibrium of the food chain, signifying their integral contribution to marine biodiversity and overall health of the ecosystem.
Scientific analysis reveals that croakers also function as regulators of their prey species' populations. By consuming smaller organisms, they help control the numbers of these species, thereby preventing potential ecological imbalance. In this light, the Atlantic croaker serves as an essential element in preserving the stability of its habitat.
Furthermore, the abundance of croakers in a particular habitat can be an indicator of the overall health of the ecosystem. Healthy croaker populations suggest a thriving marine environment, whereas a decrease may signal potential issues. Thus, the Atlantic croaker not only contributes to the ecosystem but also provides valuable information about its status. By understanding the role of the croaker, we can better appreciate the interconnectedness of our marine ecosystems and our own place within them.
Fishing Techniques for Croaker
When it comes to angling for croaker, commonly employed techniques often involve the use of bait and tackle setups along shorelines, fishing piers, and deep channels, leveraging the species' behavioral patterns and preferred habitats. The croaker's penchant for organic debris and small aquatic life forms the basis for the selection of bait.
- Bloodworms, often used as bait, are actually the larvae of the Glycera, a type of polychaete worm. Their scent and movement in water make them irresistible to croaker.
- Squid strips also serve as effective bait due to their durability and appealing scent in the water.
- Peeler crab or soft crab is another successful bait, especially during the summer months when croakers are most active.
These techniques are often most successful at specific locations within the Chesapeake Bay and tidal rivers where croakers are seasonally found. Understanding these patterns provides a sense of belonging, a shared knowledge among the angling community. Also, it's not uncommon to catch other bottom dwellers like spot and white perch while fishing for croaker, adding to the excitement of the angling experience.
Croaker in Culinary Arts

The culinary artistry surrounding croaker, a versatile species prevalent in Chesapeake Bay seafood dishes, spans various cooking methods such as grilling, frying, and baking, highlighting both its adaptability in the kitchen and its nutritional significance as a seafood choice.
As a popular saltwater fish, the croaker's robust flavour profile is enhanced by the complexity of these cooking techniques, resulting in a distinctive gastronomic experience. Its richness in essential nutrients, particularly omega-3 fatty acids and lean protein, underscores the croaker's status as a valuable component of a balanced diet.
In the realm of local cuisine tradition, the croaker's culinary versatility is further demonstrated by its presence in an array of regional recipes, each one providing a unique testament to the fish's gastronomic potential. Demand for this species in seafood markets, driven by its culinary importance, significantly contributes to its economic value within the seafood industry.
Culinary preparation of croaker, therefore, is not just about cooking a popular saltwater fish. It is about appreciating the biodiversity of our oceans, savouring a nutritious meal, and engaging in a culinary practice that connects us with the Chesapeake Bay community and its vibrant seafood culture.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is Croaker Freshwater or Saltwater?
Croaker's habitat is predominantly in saltwater environments such as bays, estuaries, and tidal rivers, rather than freshwater. This species thrives in coastal waters and is highly valued in saltwater fishing communities.
Can Croakers Live in Freshwater?
Croakers, though adaptable to varying salinity levels, are principally marine species. Freshwater environments do not support their physiological needs, making them ill-suited to such habitats despite their notable adaptability.
Can You Eat Saltwater Croaker?
Yes, Saltwater Croaker is safe for consumption. Its mild, sweet flavor and firm, flaky texture makes it a versatile choice for various cooking methods, offering a nutritious and delicious option for seafood enthusiasts.
What Kind of Fish Is a Croaker?
The Croaker, akin to a seasoned mariner, thrives in saltwater environments. Belonging to the drum family, its lifespan varies by species. It's a vital part of marine ecosystems, contributing significantly to commercial and recreational fishing.
Conclusion
In summary, the Atlantic Croaker represents a vital cog in the marine ecosystem, serving both ecological and economic roles. This saltwater fish's survival, backed by sustainable fishing practices, ensures the continuity of a rich biodiversity and the prosperity of coastal communities.
The croaker's croaking, far from being a mere idiosyncrasy, stands as a satirical reminder of their significance: even the seemingly inconsequential have a role on the grand stage of life.
