The practice of quarantining saltwater fish prior to introducing them to an established aquarium serves as a critical safeguard against potential disease transmission.
In executing this procedure, a range of elements, from the size of the quarantine tank to the specifics of equipment used, play a pivotal role.
Moreover, maintaining optimal conditions within this temporary habitat, including water quality and temperature, is fundamental to the health of the quarantined species.
Let's consider the intricacies of this process and examine the techniques that can enhance the effectiveness of fish quarantine.
Key Takeaways
- Quarantine tanks are vital for observing and acclimating new saltwater fish, reducing risk of disease transmission.
- The quarantine process requires essential equipment such as a heater, air pump, ammonia alert badge, bioballs, and bacterial culture.
- Regular maintenance, including routine water changes and monitoring of ammonia levels, is necessary for a successful quarantine process.
- Establishing and maintaining a quarantine system is cost-effective and crucial for long-term saltwater fish health management.
Understanding the Quarantine Process
The fish owner's understanding of the quarantine process is crucial in the successful acclimatization and treatment of saltwater fish. This involves a meticulous month-long observation in a separate tank equipped with essential items such as a heater, air pump, ammonia alert badge, bioballs, and a bacterial culture. The quarantine tank is a sanctuary, an isolated environment where fish can be observed and acclimated, while potential issues are addressed before introducing the marine life to the main display tank.
Rushing through the quarantine process is as detrimental as not quarantining at all, underlining the significant role of patience. The quarantine process is a safeguarding mechanism, reducing the risk of infecting the entire tank, hence preventing diseases like Uronema from decimating fish populations.
The process also necessitates routine water changes, which are pivotal for maintaining optimal water conditions. Water changes help to dilute toxins and replenish essential minerals, providing an environment conducive to the fish's health during the quarantine period. Understanding and properly implementing the quarantine process is a demonstration of commitment to maintaining a thriving aquatic ecosystem and fosters a sense of belonging among fish owners.
Importance of Quarantine Tanks
The importance of quarantine tanks in maintaining the health of saltwater fish cannot be overemphasized. These tanks serve as a cost-effective barrier against the spread of diseases and parasites, mitigating the risk of potentially devastating outbreaks such as Uronema.
Establishing a well-regulated quarantine system early on in the hobby can significantly enhance the effectiveness of these preventative measures, ensuring the longevity and well-being of the fish population.
Benefits of Quarantine Tanks
In the realm of marine aquarium keeping, quarantine tanks play an indispensable role, significantly reducing the risk of introducing diseases and parasites to the main display tank. These isolated environments provide a safe space for observing and treating new fish, without endangering the already established community.
A quarantine tank can be a cost-effective measure, alleviating the need to treat an entire tank for a bacterial infection. It's a proficient defense against common fish diseases like Uronema, as it allows for targeted isolation and treatment.
Developing a routine of quarantine early in the hobby is not just a preventative measure, but also a commitment to maintaining overall fish health, fostering a sense of belonging within the aquarium community.
Establishing a Quarantine System
Why is establishing a quarantine system integral to the health of your aquarium's inhabitants?
Quarantine tanks play a crucial role in preventing the transmission of diseases and parasites from newly introduced fish to the established marine life in your aquarium.
This quarantine saltwater system significantly reduces the risk of widespread infections, thereby maintaining the overall health of your aquarium's ecosystem.
Incorporating a routine of medicated food and regular water change in your quarantine protocol can further enhance its efficacy.
It is far more cost-effective and less devastating than having to replace an entire fish population due to an uncontrolled outbreak like Uronema infection.
Thus, developing an early habit of quarantine practices is paramount for long-term fish health management.
Preventing Disease Transmission
Employing quarantine tanks serves as an effective shield against disease transmission, primarily by secluding new fish from the existing aquatic population. Quarantine tanks offer a controlled environment to observe, acclimatize, and treat new fish, ensuring their health and reducing the risk of disease transmission.
- Quarantine tanks provide an isolation space, preventing immediate contact with the established aquatic life and potential disease spread.
- They allow for careful observation of new fish for any signs of disease or parasites.
- Quarantine tanks facilitate a gradual acclimation process for new fish, reducing stress-induced diseases.
- They offer a controlled environment for any necessary treatments, preventing the entire tank's exposure to medications.
Adopting quarantine practices is not just a preventive measure; it is a responsible step towards sustaining a healthy aquatic ecosystem.
Choosing the Right Quarantine Tank
The selection of an appropriate quarantine tank is contingent on the number and species of saltwater fish, with capacity typically ranging from 10-40 gallons. It is paramount to outfit the tank with essential equipment including a heater, air pump, ammonia alert badge, established bioballs, and a starter bacterial culture.
Notably, the tank should be devoid of live rock or decorations to prevent copper absorption during treatment, while secure lids and PVC tube hiding spots can mitigate stress and prevent escape.
Selecting Tank Size
In the realm of saltwater fish quarantine, the selection of an appropriately sized tank – ranging typically from 10-40 gallons for small to medium fish – is a critical factor in providing a stress-free environment during the quarantine period. The importance of size selection cannot be overstated, as it directly influences the wellbeing of the fish during this potentially stressful time.
To make the best decision regarding tank size, consider the following aspects:
- The size and number of fish to be quarantined
- The species' natural behavior and space requirements
- The larger the fish, the larger the quarantine tank needed
- Single small fish can comfortably inhabit a 10-gallon tank, while multiple or larger fish may require a 20-40 gallon tank
Essential Quarantine Equipment
Equipping your quarantine tank with the right tools and equipment plays a critical role in ensuring the health and survival of your saltwater fish during the quarantine period.
The essential gear includes a reliable Heater and Thermometer, which maintains a stable temperature, vital for fish wellbeing.
A Sponge Filter coupled with an air pump provides effective biological filtration, keeping the water clean and free of toxins.
Copper test kits monitor copper levels, as absorption by live rocks, if used, can lead to toxic conditions.
Additionally, refractometers measure salinity, another key parameter for saltwater species.
Incorporating non-absorbent hiding spots like PVC tubes and a secure lid will help create a safe and stress-free environment for your aquatic pets.
Essential Quarantine Equipment
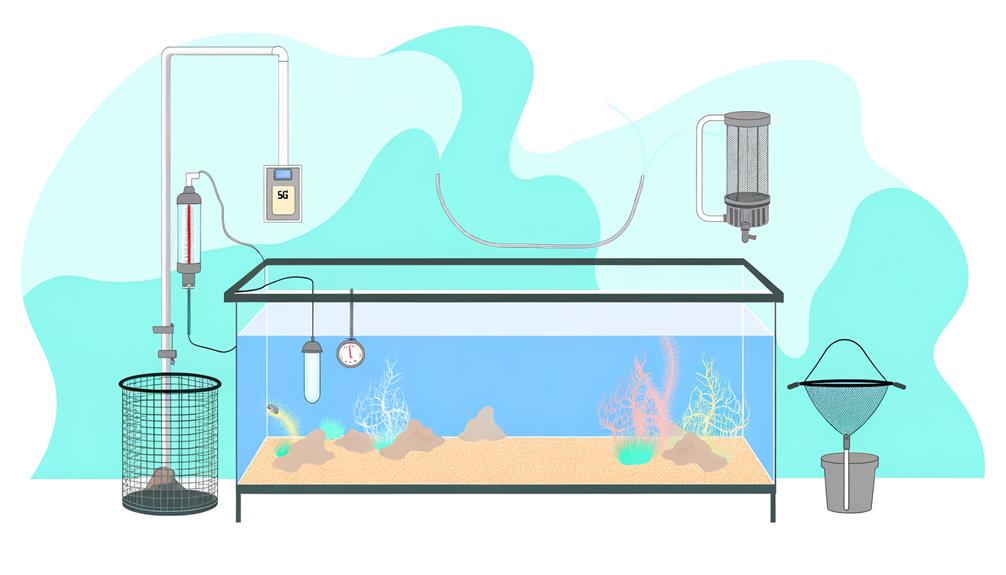
For the successful quarantine of saltwater fish, essential equipment such as a heater, thermometer, sponge filter, and air pump are of paramount importance. These tools are foundational in creating a stable and controlled environment when you quarantine new fish. Equally critical are devices like the Ammonia Alert badge and test kits to monitor the copper level, which ensure the security of the quarantine tank's inhabitants.
- Heater and Thermometer: These devices regulate and measure the temperature in the quarantine tank, creating an optimal environment for the fish.
- Sponge Filter and Air Pump: These components maintain water quality by filtering out impurities and providing adequate oxygenation.
- Ammonia Alert Badge: This tool provides an immediate and continuous reading of ammonia levels, which can be toxic to fish.
- Copper Test Kits: These kits measure the copper level in the tank, which is essential when treating fish for certain parasites.
In essence, the quarantine process requires a meticulous and scientific approach to ensure the wellbeing of saltwater fish. Utilizing necessary equipment, timely monitoring, and accurate testing will result in a successful quarantine experience.
Preparing Your Quarantine Tank
Having established the necessary equipment for successful quarantine, the next vital step involves the careful preparation of your quarantine tank. The size of the tank should range between 10-40 gallons, depending on the number of saltwater fish you intend to quarantine.
Achieving a conducive environment within the quarantine tank involves a few essential elements. These include a heater, an air pump, an ammonia alert badge, the use of bioballs, and a bacterial culture. These pieces of equipment contribute significantly to the successful habitation of saltwater fish in the quarantine tank.
| Equipment | Purpose | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Heater | Maintains optimal temperature | Prevents thermal stress |
| Air Pump | Ensures sufficient oxygen supply | Avoids hypoxic conditions |
| Ammonia Alert Badge | Monitors ammonia levels | Prevents toxic environment |
The absence of live rock or decorative items is deliberate to prevent copper absorption. However, the inclusion of PVC tubes provides necessary hiding spots for the fish. A secure lid is also crucial to prevent fish from jumping out.
Introducing Fish to Quarantine
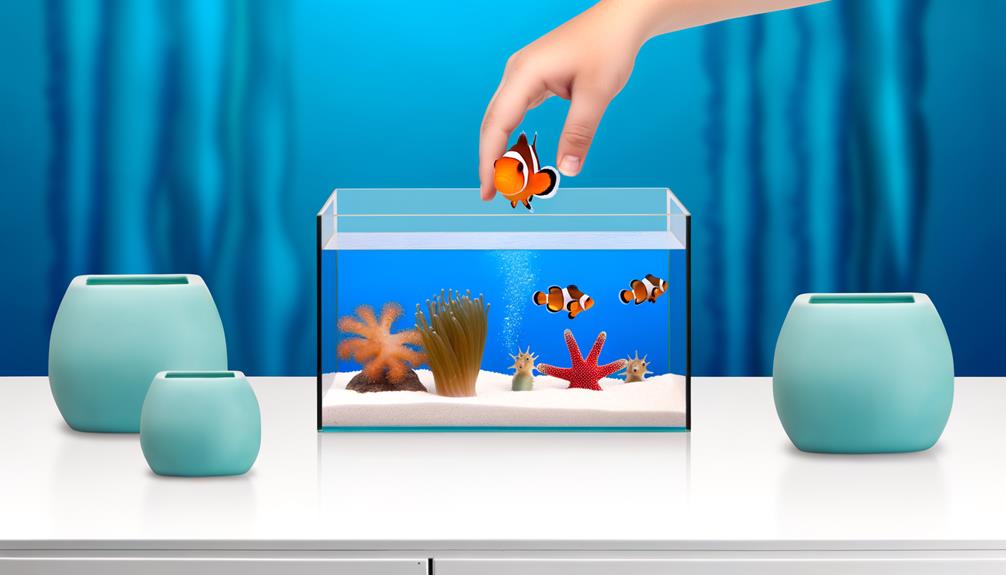

After carefully setting up the quarantine tank, the next critical process involves the methodical introduction of saltwater fish to this new environment. This step is crucial as sudden changes in water conditions can be stressful for fish, potentially leading to illness or even death. Therefore, it is paramount to acclimate fish to the quarantine tank gradually to ensure a smooth transition.
The following steps are suggested to minimize stress when fish are added:
- Start by placing the bagged fish in the quarantine tank to allow for temperature acclimation.
- Gradually add small amounts of tank water into the bag over a period of 1-2 hours.
- After this, gently release the fish into the quarantine tank, avoiding any water from the bag.
- Provide plenty of hiding places in the tank to offer a sense of security.
Monitoring the behavior of the fish is essential during this phase. Signs of distress, unusual aggression, or changes in feeding habits could signify problems. The quarantine tank should not be overcrowded to maintain optimal water quality and reduce competition, ensuring each fish's healthy transition into the new environment.
Monitoring Fish Health in Quarantine
In the quarantine phase, diligent observation of the saltwater fish's behavior and physical condition is critical to identify early signs of stress, illness, or environmental discomfort. Key aspects to monitor include changes in swimming patterns, physical appearances such as lesions, discoloration, or fin damage, as well as feeding habits.
It's equally vital to keep a close eye on water parameters. Regular testing for ammonia, nitrite, nitrate, pH, and salinity levels ensures that the quarantine environment remains stable and suitable for the fish. Any drastic or sudden changes could lead to stress or disease.
Here is a simplified guide to monitoring fish health:
| Monitoring Aspect | Significance |
|---|---|
| Behavior | Indication of stress or illness |
| Physical Appearance | Signs of disease or injury |
| Feeding Habits | Gauge of fish's overall health |
| Water Parameters | Assessment of environment suitability |
Any signs of disease, parasites, or infections like white spots, velvet, or fin rot should be red flags that require immediate attention. By closely monitoring fish health during quarantine, you're ensuring a smooth transition to the main tank, contributing to a thriving aquatic community.
Transitioning Fish to Main Tank
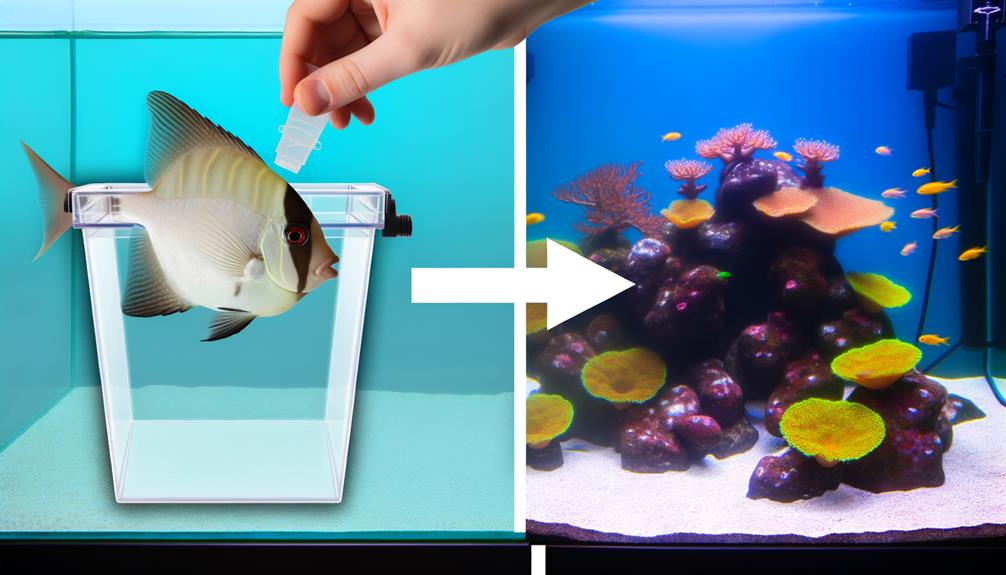
Once the quarantine period is successfully completed, the process of transitioning the saltwater fish to the main tank necessitates careful acclimatization to mitigate potential shock and stress. This involves gradually introducing the new water conditions to acclimate fish smoothly. The transition is not just a physical move; it's a careful process that involves continuous monitoring of water parameters and fish behavior.
The acclimation process can be summarized in four key steps:
- Gradually introduce the fish to the new water conditions of the main tank over a period to avoid shock.
- Monitor the behavior of the fish closely upon introduction to the main tank, to check for signs of aggression or territorial disputes.
- Regularly check the water parameters in both the quarantine and main tanks to ensure a seamless transition.
- Introduce the fish during feeding time in the main tank to distract existing inhabitants and reduce initial aggression.
Post-transition, continue to monitor behavior and health for any signs of stress or disease. The goal is to ensure that the fish not only survives the transition but thrives in its new environment, contributing to a healthy and vibrant aquatic community.
Common Quarantine Mistakes to Avoid
While ensuring a smooth acclimatization process is crucial, it is equally important to avoid certain common mistakes during the quarantine period that could potentially compromise the health of the saltwater fish and the overall aquatic ecosystem.
A prevalent error is not quarantining fish for at least 4 weeks. This period is essential for detecting latent diseases that might otherwise infiltrate the main tank. Also, using unestablished or inadequate filtration systems in the quarantine tank could lead to poor water quality, thereby compromising the fish's health.
Another critical oversight is the neglect of appropriate water parameters. Inconsistent salinity and temperature can cause undue stress to fish, leading to weakened immunity and susceptibility to diseases. Introducing multiple new fish at once without individual quarantine can also precipitate disease outbreaks due to increased pathogenic load.
Lastly, a daily observation of fish behavior and physical symptoms is indispensable during quarantine. Neglecting this step can delay treatment for potential issues, causing unnecessary harm to the fish. Hence, careful monitoring of the quarantine tank, water parameters, and fish behavior during the quarantine period can ensure a healthy and thriving saltwater aquarium.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Should I Quarantine My Saltwater Fish?
Saltwater fish should typically be quarantined for at least 4 weeks. This duration allows for disease identification, appropriate medication usage, and observation of feeding practices, which are crucial for ensuring fish health and tank stability.
How Do You Set up a Quarantine Tank for Saltwater Fish?
Setting up a quarantine tank involves careful tank maintenance, including the selection of a suitable substrate. Attention to temperature control is critical. This ensures a stable, stress-free environment, fostering a sense of belonging for the fish.
What Is the Best Way to Quarantine Fish?
The optimal quarantine method involves a careful acclimation process, tailored quarantine diet, and appropriate use of fish medications. This strategic approach ensures the overall health and wellbeing of the fish, minimizing potential disease transmission.
How Long Should I Quarantine Fish With Ich?
For effective ich treatment, the disease progression must be interrupted. Quarantine fish with ich for a minimum of 76 days to ensure medication effectiveness and break the parasite's life cycle, thus preventing further outbreaks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the implementation of a meticulous quarantine practice is an indispensable safeguard in saltwater fishkeeping. This procedure, underpinned by scientific principles and precision, mitigates the risk of disease transmission, ensuring the maintenance of an optimal aquatic environment.
The quarantine process demands patience and careful observation, but the reward is a vibrant, disease-free main tank. It is a testament to the adage, 'an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.'
